AI聊天盒子 - 集成语音转文字服务
前言
好久没有更新文章了,最近在做一个智能键盘的项目,以后有机会给大家介绍。前面我们已经实现了和AI聊天的功能,然而我们还需要将用户的语音转成文字发送给AI,本文介绍如何集成语音转文字服务。
本系列其他文章
语音转文字服务
语音转文字服务有很多成熟的项目可以使用,我选择了Vosk语音识别工具包。要使用Vosk,可以通过pip安装Vosk模块,另外还需要从链接vosk-model-cn-0.22.zip下载模型文件,解压后待用。
pip install vosk flask flask-cors
结合Flask模块我们就可以快速实现一个基于Vosk的REST服务,创建一个名为vosk_server.py的文件,填入下列代码。
import tempfile
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app) # 允许跨域请求(局域网内其他设备访问)
# 加载Vosk模型(替换为你的模型路径)
model = Model("vosk-model-cn-0.22") # 中文模型
@app.route('/transcribe', methods=['POST'])
def transcribe():
if 'file' not in request.files:
return jsonify({"error": "No audio file provided"}), 400
audio_file = request.files['file']
_, temp_path = tempfile.mkstemp(suffix=".wav")
audio_file.save(temp_path)
# 使用Vosk进行语音识别
recognizer = KaldiRecognizer(model, 16000)
with open(temp_path, 'rb') as f:
audio_data = f.read()
recognizer.AcceptWaveform(audio_data)
os.remove(temp_path) # 删除临时文件
result = recognizer.FinalResult()
return result
#return jsonify({"text": result[0]})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000) # 允许局域网访问
我们到目录vosk-model-cn-0.22的上一级目录下运行 python vosk_server.py ,我们就启动了一个简单的语音转文字服务。这个语音转文字服务,接受一个wav文件,然后将语音转换成文字返回给调用者。我们可以使用下面的命令来测试这个REST服务。
curl -X POST -F "file=@record.wav" http://127.0.0.1:5000/transcribe
集成语音转文字服务
在AI聊天盒子 - 使用esp-sr和Rust语言编写语音识别程序中我们已经实现了一个简单的AI对话流程。这里我们先回顾一下这个流程。
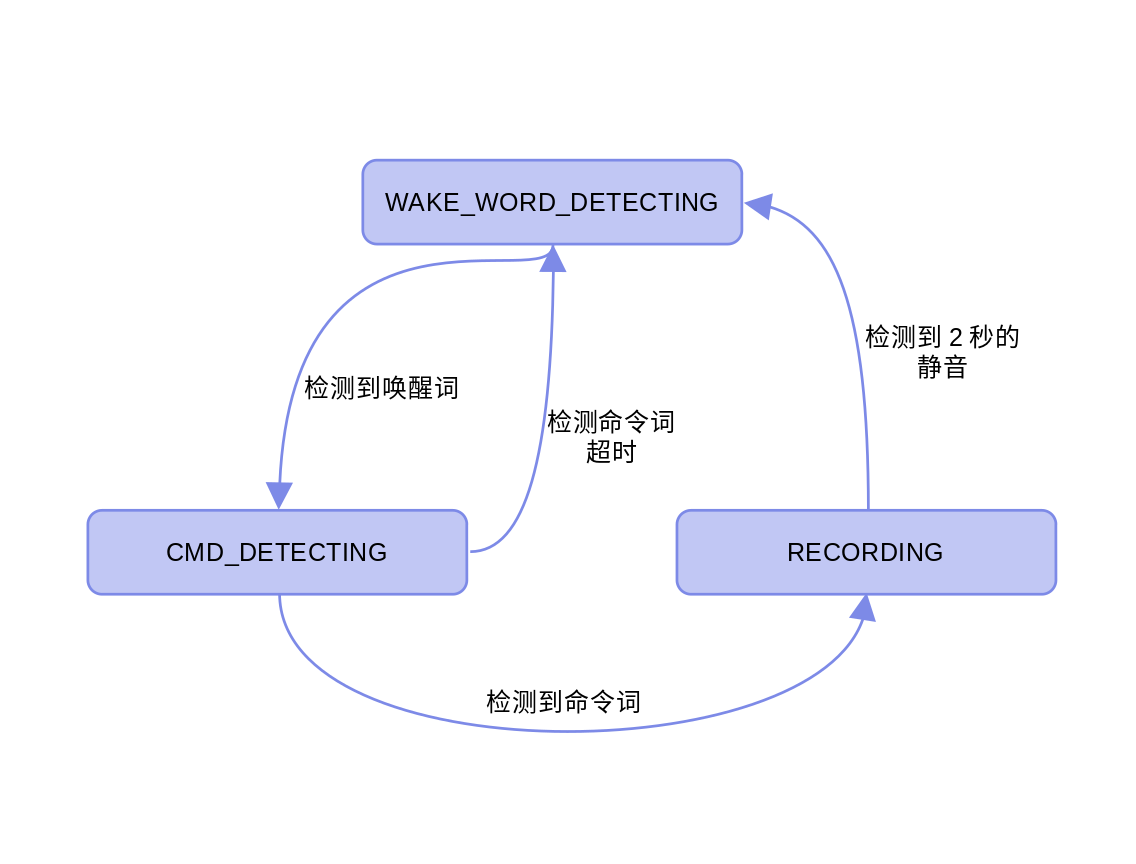
- 用户需要先使用唤醒词“hi, 乐鑫”唤醒程序。
- 用户再使用命令词“我有个问题”进入录音状态。
- 记录用户的语音。
- 程序检测到2秒连续的静音,返回等待唤醒检测的状态。
我将第4步进行了扩展,检测到2秒连续的静音后,我们就会开始语音转换流程。然后将转换结果发送给LLM,再获取并在日志中打印LLM的回答。扩展后的流程如下。
- 用户需要先使用唤醒词“hi, 乐鑫”唤醒程序。
- 用户再使用命令词“我有个问题”进入录音状态。
- 记录用户的语音。
- 程序检测到2秒连续的静音:
- 使用语音转文字服务将语音转换为文字。
- 得到文字形态而问题后,使用LLM API向DeepSeek提问。
- 获得回答打印到日志中。
为了实现增加的功能我创建了一个transcription_worker线程负责将语音转换成文字和向LLM提问,这样可以减少对fetch_proc的影响,保证AFE数据队列不会堵塞。
// Worker function for the transcription thread
fn transcription_worker(rx: Receiver<TranscriptionMessage>) -> anyhow::Result<()> {
log::info!("Transcription worker thread started");
// Get token from environment variable at compile time
let token = env!("LLM_AUTH_TOKEN", "LLM authentication token must be set at compile time");
// Create and configure the LLM helper
let mut llm = match llm_intf::LlmHelper::new(token, "deepseek-chat") {
helper => {
log::info!("LLM helper created successfully");
helper
}
};
// Configure with parameters suitable for embedded device
llm.configure(
Some(512), // Max tokens to generate in response
Some(0.7), // Temperature - balanced between deterministic and creative
Some(0.9) // Top-p - slightly more focused sampling
);
// Send initial system message to set context
llm.send_message(
"接下来的请求来自一个语音转文字服务,请小心中间可能有一些字词被识别成同音的字词。".to_string(),
ChatRole::System
);
log::info!("LLM helper initialized with system prompt");
loop {
match rx.recv() {
Ok(TranscriptionMessage::TranscribeFile { path }) => {
log::info!("Received request to transcribe file: {}", path);
match transcribe_audio(&path) {
Ok(transcription) => {
log::info!("Transcription completed: {}", transcription);
// Send the transcription to the LLM
log::info!("Sending transcription to LLM...");
let response = llm.send_message(transcription, ChatRole::User);
if response.starts_with("Error:") {
log::error!("LLM API error: {}", response);
} else {
log::info!("LLM response: {}", response);
// Here you would send the response to a text-to-speech system
// For now, we just log it
}
},
Err(e) => {
log::error!("Failed to transcribe audio: {}", e);
}
}
},
Ok(TranscriptionMessage::Shutdown) => {
log::info!("Transcription worker received shutdown signal");
break;
},
Err(e) => {
log::error!("Error receiving message in transcription worker: {}", e);
break;
}
}
}
log::info!("Transcription worker thread terminated");
Ok(())
}
并在inner_fetch_proc的Recording状态中通过管道给transcription_worker发送消息,触发语音转换流程。
// Finalize WAV file
if let Some(writer) = wav_writer.take() {
log::info!("Finalizing WAV file after {} silent frames", silence_frames);
writer.finalize()?;
// Flush the filesystem to ensure all data is written
if let Err(e) = flush_filesystem("/vfat") {
log::warn!("Failed to flush filesystem: {}", e);
} else {
log::info!("Filesystem flushed successfully");
// Send a message to the transcription thread to process the file
let file_path = format!("/vfat/audio{}.wav", file_idx - 1);
if let Err(e) = arg.transcription_tx.send(TranscriptionMessage::TranscribeFile { path: file_path }) {
log::error!("Failed to send transcription message: {}", e);
} else {
log::info!("Sent audio file for asynchronous transcription");
}
}
}
具体的代码修改可以查看代码仓ai-chatbox。
效果测试
我还是使用XIAO ESP32S3 Sense作为测试硬件。为了避免手动刷写模型文件,我把srmodels存到了SD卡上,除了代码修改中包含的配置文件skconfig.defaults的修改和将esp_srmodel_init的参数改为“/vfat”之外,还要把srmodels中的四个子目录mn7_cn、nsnet2、vadnet1_medium、wn9_hilexin整体拷贝到SD卡的根目录下。
> ls ./target/xtensa-esp32s3-espidf/debug/build/esp-idf-sys-*/out/build/srmodels
fst mn7_cn nsnet2 srmodels.bin vadnet1_medium wn9_hilexin
但这个修改其实不是必须的,主要是为了刷写固件更加方便。下面运行 env WIFI_SSID=<ssid-name> WIFI_PASS=<wifi-password> LLM_AUTH_TOKEN=<llm-auth-token> cargo espflash flash -p /dev/ttyACM0 --flash-size 8mb 命令刷写好固件,再用 cargo espflash monitor 查看运行日志。下面是我测试时的运行日志,我问了DeepSeek一个问题“大模型是什么东西”。不过可能由于Vosk模型比较小,发音需要比较清楚才能准确识别。
I (61892) ai_chatbox: State transition: WakeWordDetecting -> CmdDetecting (Waiting for wake word → Detecting command): Wake word detected
I (64512) ai_chatbox: Command detected: 1
I (64512) ai_chatbox: State transition: CmdDetecting -> Recording (Detecting command → Recording audio): Command detected (ID: 1)
I (64522) ai_chatbox: Creating WAV file: /vfat/audio1.wav
I (70822) ai_chatbox: State transition: Recording -> WakeWordDetecting (Recording audio → Waiting for wake word): Detected 66 frames of silence
I (70822) ai_chatbox: Finalizing WAV file after 66 silent frames
I (70852) ai_chatbox: Filesystem at /vfat flushed successfully
I (70852) ai_chatbox: Filesystem flushed successfully
I (70852) ai_chatbox: Received request to transcribe file: /vfat/audio1.wav
I (70862) ai_chatbox: Sent audio file for asynchronous transcription
I (70862) ai_chatbox: Transcribing audio file: /vfat/audio1.wav
I (71132) ai_chatbox: Read 205868 bytes from WAV file
I (72612) ai_chatbox: Response status: 200
I (72612) ai_chatbox: Transcription completed: {
"text" : "大 模型 是 什么 东西"
}
I (72612) ai_chatbox: Sending transcription to LLM...
I (72622) ai_chatbox::llm_intf: Sending request to DeepSeek API...
I (72622) ai_chatbox::llm_intf: Initiating HTTP request to https://api.deepseek.com/chat/completions
I (72772) esp-x509-crt-bundle: Certificate validated
I (73462) ai_chatbox::llm_intf: HTTP request sent successfully.
I (73462) ai_chatbox::llm_intf: HTTP response status: 200
I (94142) ai_chatbox::llm_intf: Response received. Tokens used: 124 (prompt) + 390 (completion) = 514 (total)
I (94142) ai_chatbox: LLM response: **大模型(Large Language Model, LLM)** 是一种基于海量数据训练的**人工智能模型**,能够理解和生成人类语言(甚至代码、多模态内容等)。它的核心特点是:
---
### 1. **本质是什么?**
- **参数规模超大**:通常拥有百亿、千亿甚至万亿级参数(比如GPT-3有1750亿参数),通过深度学习(如Transformer架构)从文本数据中学习语言规律。
- **通用性强**:不像传统AI专精单一任务(如翻译),大模型能处理问答、写作、编程、逻辑推理等多种任务。
---
### 2. **为什么叫“大”?**
- **数据大**:训练数据可达TB级(全网文本、书籍、代码等)。
- **算力大**:需要超算级GPU集群训练,成本极高(例如GPT-3训练费用超千万美元)。
- **能力“大”**:涌现出小模型不具备的复杂能力(如上下文学习、少样本推理)。
---
### 3. **常见例子**
- **ChatGPT**(OpenAI)、**Gemini**(Google)、**Claude**(Anthropic)等对话式AI。
- **文心一言**(百度)、**通义千问**(阿里)等中文大模型。
---
### 4. **能干什么?**
- 生成文章、代码、剧本
- 解答复杂问题(需验证)
- 翻译/总结文档
- 作为智能助手(客服、教育等)
---
### 5. **局限性**
- 可能产生“幻觉”(编造错误信息)
- 依赖训练数据,存在偏见风险
- 需大量算力,不够环保
如果需要更具体的解释(如技术原理、应用场景),可以告诉我!
总结
本文主要考虑如何为ai-chatbox集成语音转文字服务,这样我们就可以用语音向LLM提问。如果进一步将获得的回答转成语音播放出来,就可以完整地和LLM语音聊天了,这将是下一篇文章我们要考虑的事情。
链接
- vosk-model-cn-0.22.zip - https://alphacephei.com/vosk/models/vosk-model-cn-0.22.zip
- ai-chatbox - https://github.com/paul356/ai-chatbox